
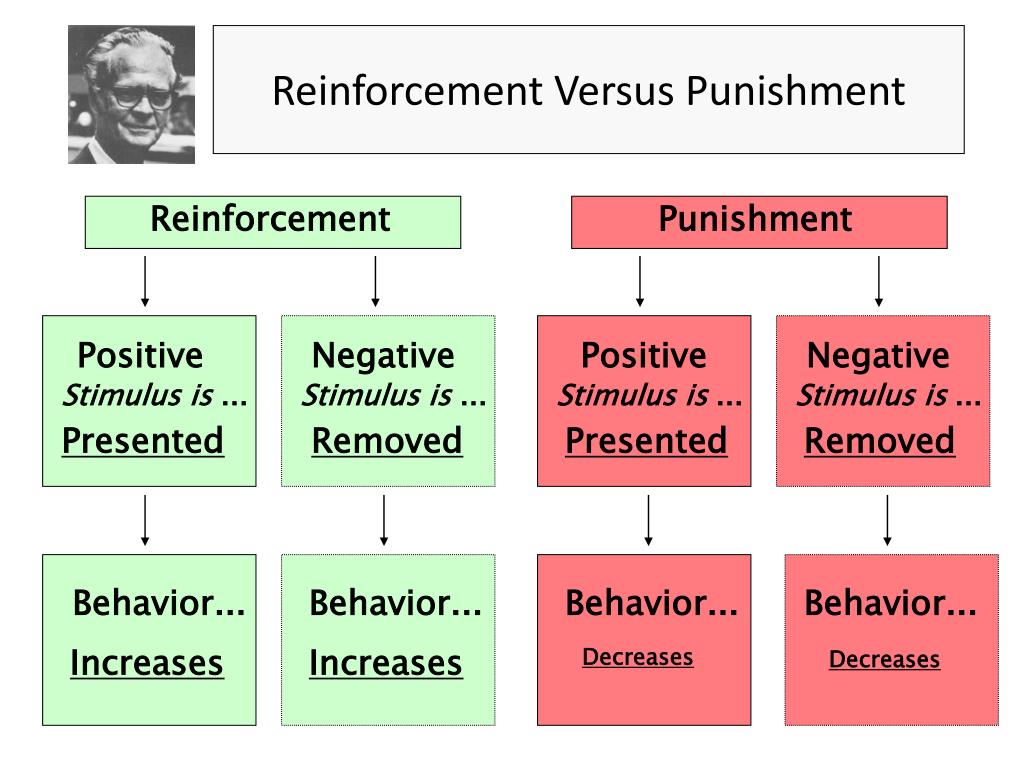
An example is reprimanding a player after a mistake or making an athlete do push-ups or sprints after a fumble. Positive punishment is the presentation of an act, object, or event following a behavior that could decrease the behavior’s occurrence. Punishment, on the other hand, is designed to decrease the occurrence of a given operant, that is, negative behaviors such as mistakes or a lack of effort. This coaching reinforcement style focuses attention on what the athlete is doing correctly. For example, if the team showed great hustle in practice (i.e., the operant is enthusiasm and hustle), then the coach could announce that no wind sprints would be required at the session’s end. Negative reinforcement also increases the probability of occurrence of a given operant, but it is accomplished through the removal of an act, object, or event that is typically aversive. Positive reinforcement is the act of increasing the probability of occurrence of a given behavior (a target behavior, such as correct footwork in basketball, is termed an operant) by following it with a positive action, object, or event such as praise, decals on the helmet, or prizes and awards.

All text and images provided by Human Kinetics.Ĭoaches can also benefit from understanding the concepts of positive and negative reinforcement and positive and negative punishment as they relate to motivation (22). The following is an exclusive excerpt from the book Essentials of Strength Training and Conditioning-4th Edition With Web Resource, published by Human Kinetics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
